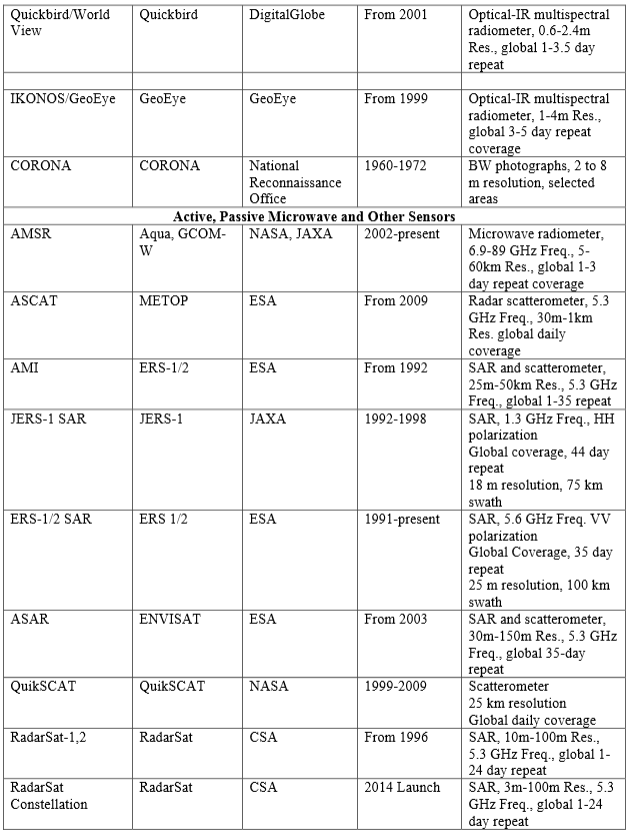
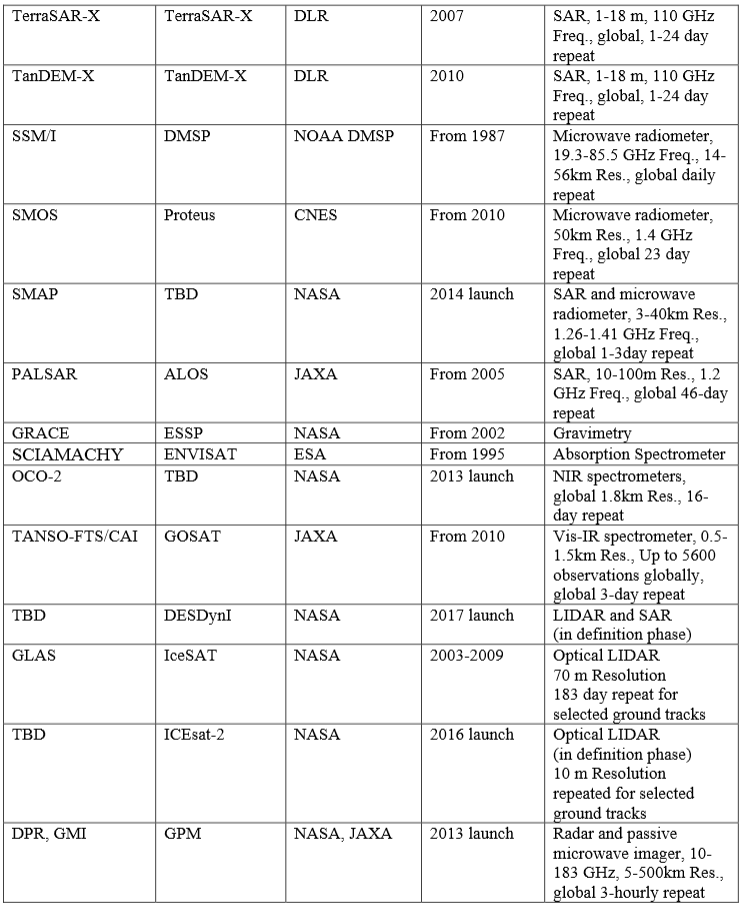
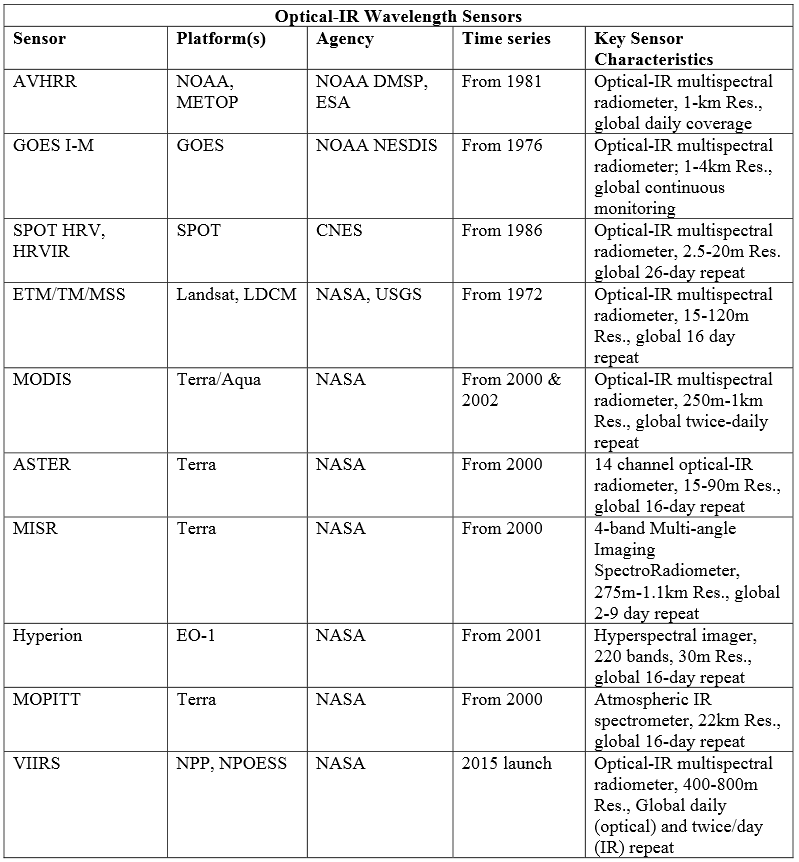
Below is a list of airborne and spaceborne satellite systems that is being used by Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE), which is an international research initiative led by NASA. ABoVE is designed to produce new knowledge needed to understand how climate change impacts ecosystems in the High Northern Latitude region, and how these changes produce feedbacks to climate and are influencing ecosystem services.
The project emphasizes on seven science themes, namely, Disturbance, Permafrost, Surface Hydrology, Ecosystem Dynamics, Soil Carbon, Land-Atmosphere Feedbacks, and Human Dimensions / Impacts Assessment.
“…these science themes will address the key uncertainties on the processes that are driving changes to ecosystems in the High Northern Latitude (HNL) region, as well as the impacts of these changes. The studies conducted for ABoVE will focus on identifying thresholds and tipping points that can produce state changes in how Arctic and Boreal ecosystems in response to variations in climate, providing the basis for improving the reliability of the process models required to predict how these ecosystems are likely to change in the future based on different climate change scenarios.”
Airborne & Sub-orbital platforms and sensors (click the image for larger view)

Spaceborne satellite systems (click the image for larger view)
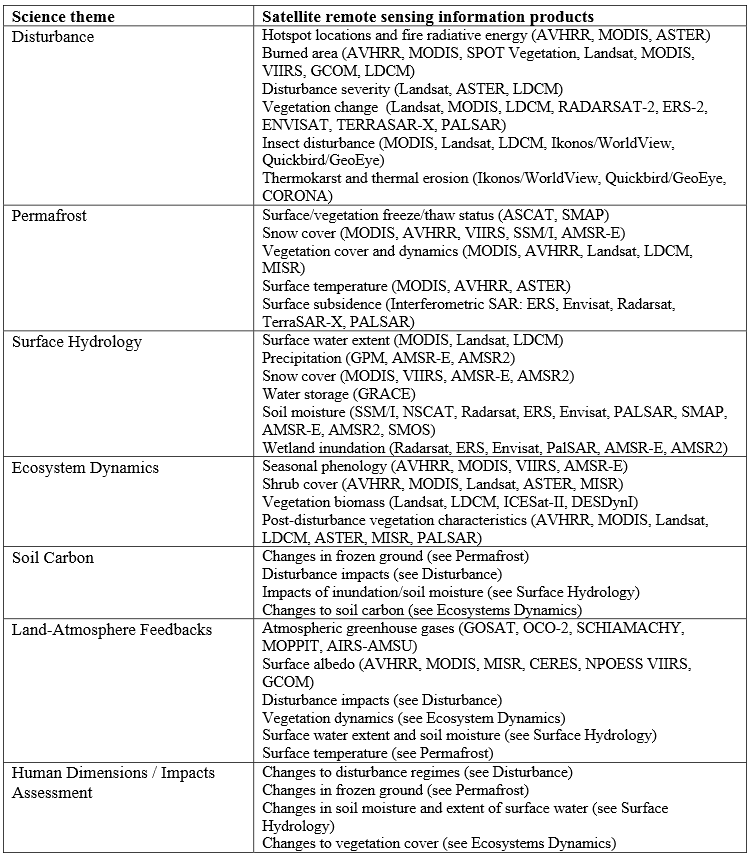
Also, here is a summary of information products derived from previous and existing satellite remote sensors, or those scheduled for launch in the near term (by 2015) that provide the foundation for the ABoVE Science Theme questions. (click the image for larger view)
You can read more about the ABoVE project here.